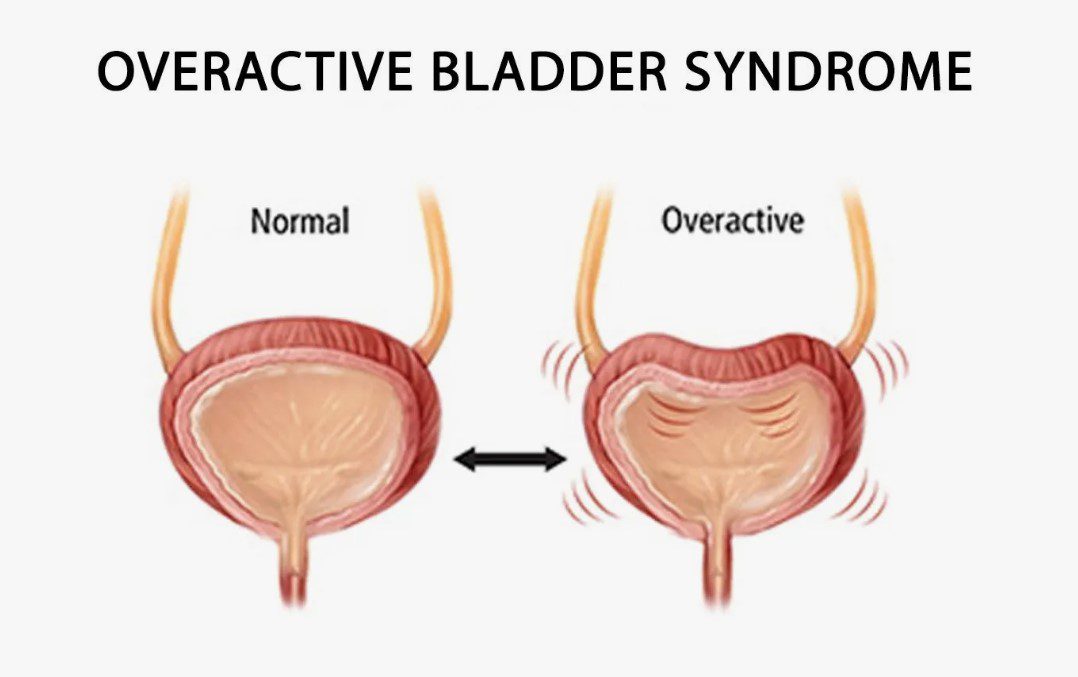
An overactive bladder (OAB) can be an inconvenient and often frustrating condition, impacting both physical and emotional well-being. It involves a frequent and sudden urge to urinate that is difficult to control, sometimes resulting in unintentional loss of urine. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, especially as they age, but it is by no means limited to older adults. Understanding OAB and knowing how to manage it effectively can significantly enhance one’s quality of life.
In this article, we will discuss practical tips and tricks for managing an overactive bladder. Additionally, for those seeking specialized medical assistance, the Urology Partners of North Texas offer advanced treatment options and expert guidance to help manage OAB more effectively.
Understanding Overactive Bladder
Before diving into management techniques, it’s essential to understand what OAB is and what causes it. Overactive bladder is primarily characterized by an urgency to urinate, often accompanied by increased frequency and nocturia (waking up multiple times at night to urinate). This urgency is caused by involuntary bladder muscle contractions, which can occur even when the bladder isn’t full. Although the exact cause of OAB can vary from person to person, contributing factors often include:
- Weak bladder muscles
- Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s or multiple sclerosis
- Certain medications or diuretics
- Urinary tract infections
- Hormonal changes, especially in postmenopausal women
- Diet and lifestyle choices
While OAB is more common among older adults, it can also affect younger individuals due to factors like stress, dietary habits, and lifestyle choices. If you experience symptoms of OAB, consult with healthcare professionals, such as those at Urology Partners of North Texas, who are well-equipped to assess and provide individualized treatment plans for your condition. Visit: sumssolution.com
Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing OAB
- Monitor Your Fluid Intake Adjusting fluid intake is a practical approach to managing OAB symptoms. Drinking too much or too little water can exacerbate symptoms. Aim for balanced hydration by drinking moderate amounts of water throughout the day, and try to avoid excessive intake in the evening to minimize nocturia.
- Avoid Bladder Irritants Certain foods and drinks can irritate the bladder lining and trigger OAB symptoms. Common irritants include:
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Carbonated drinks
- Citrus fruits
- Spicy foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- Eliminating or reducing these items from your diet can help alleviate the urgency and frequency associated with OAB.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight Excess body weight places additional pressure on the bladder and pelvic muscles, which can worsen OAB symptoms. Regular physical activity and a balanced diet can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing strain on the bladder.
- Implement Bladder Training Techniques Bladder training, or scheduled voiding, involves gradually extending the time between urinating to improve bladder control. Start by setting a schedule for bathroom breaks every two hours, then slowly increase this interval as your bladder becomes more accustomed to holding urine. Over time, this can help reduce the frequency and urgency of OAB.
- Practice Pelvic Floor Exercises Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises like Kegels can help improve bladder control. To perform a Kegel, contract the muscles you would use to stop urinating, hold for a few seconds, and then release. Repeat these exercises daily to build muscle strength and increase bladder support.
- Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Stress and anxiety can worsen OAB symptoms, as they can lead to overactivity of the bladder muscles. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help relax the mind and body, ultimately reducing bladder spasms and urgency.
Medical Treatments for Overactive Bladder
If lifestyle changes alone aren’t enough, there are several medical treatments that can help manage OAB:
- Medications There are medications designed to relax the bladder muscles and reduce urinary urgency. Anticholinergic medications, such as oxybutynin and tolterodine, can reduce bladder contractions. Another class of drugs, beta-3 adrenergic agonists (like mirabegron), helps the bladder hold more urine.
- Botox Injections Botox injections are a more recent treatment option for OAB. Botox works by paralyzing certain bladder muscles, which reduces involuntary contractions and can help alleviate OAB symptoms. This treatment is generally effective for three to six months before needing a repeat injection.
- Nerve Stimulation (Neuromodulation) Neuromodulation is a treatment that involves stimulating nerves responsible for bladder control, such as the sacral nerve or the tibial nerve. Sacral neuromodulation is a procedure where a small device is implanted to send electrical pulses to the bladder nerves, helping to restore normal function. This can be a long-term solution for those who haven’t had success with other treatments.
- Surgery In extreme cases, when all other treatments have failed, surgical options are available. These procedures may include bladder augmentation or urinary diversion. Surgery is generally a last resort and requires careful consideration and consultation with a urologist.
Additional Tips and Tricks for Managing OAB
- Keep a Bladder Diary Keeping track of your urination patterns, fluid intake, and any bladder-related symptoms can help you identify triggers and better understand your bladder’s behavior. This information is also helpful when discussing your symptoms with a healthcare provider.
- Wear Absorbent Pads or Underwear For some, managing OAB may involve wearing absorbent pads or specialized underwear to prevent embarrassment or discomfort from leakage. These products have become discreet and comfortable, allowing for confidence and freedom during daily activities.
- Develop a Bathroom Routine Establishing a routine can help train your bladder. For example, try to urinate every two to three hours, even if you don’t feel the urge. This practice can help reduce the frequency of urgent episodes and give you more control over your bladder.
- Stay Positive and Patient Managing OAB is a gradual process, and it’s essential to be patient. Some days may be easier than others, but staying committed to your routine and making small adjustments along the way will help. Remember, you’re not alone—OAB is a common condition, and there are numerous resources available to support you.
Getting Professional Help
While lifestyle changes and treatments can significantly help manage OAB symptoms, consulting a specialist can provide additional support and guidance tailored to your specific needs. UPNT offers comprehensive and advanced treatment options for those dealing with overactive bladder and other urological issues.