Introduction
Nerve Damage also known as neuropathy, is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can result from a variety of causes, including diabetes, injuries, infections, and autoimmune diseases. Understanding the signs of knowing how to treat it effectively can significantly improve your quality of life.
What Is Nerve Damage?
Nerve Damage occurs when the nerves in your body are injured or diseased, disrupting their ability to send signals to and from the brain. This can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain and disability.
Types of Nerve Damage
There are three main Types of Nerve Damage, each affecting different parts of the nervous system:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: This type of affects the peripheral nerves, which are located outside the brain and spinal cord. It is the most common form of neuropathy and often affects the hands and feet.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: This type of nerve damage impacts the autonomic nerves, which control involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and bladder control.
- Proximal Neuropathy: This type of nerve damage affects the nerves in the thighs, hips, or buttocks. It is less common than peripheral neuropathy but can be more debilitating.
Signs and Symptoms of Nerve Damage
Recognizing the signs of nerve damage is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. The symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the, but some common signs include:
- Numbness and Tingling: One of the most common symptoms is a sensation of numbness or tingling, often described as a “pins and needles” feeling.
- Pain: Nerve damage can cause a range of pain sensations, from a dull ache to sharp, shooting pains. The pain may be constant or intermittent and can be exacerbated by certain activities or positions.
- Muscle Weakness: Damaged nerves can lead to muscle weakness, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as walking, gripping objects, or lifting weights.
- Loss of Coordination: Nerve damage can affect your balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls and injuries. You may find it difficult to walk in a straight line or perform tasks that require fine motor skills.
- Sensitivity to Touch: Some people with nerve damage experience heightened sensitivity to touch, known as allodynia. Even light pressure or gentle touch can cause significant discomfort or pain.
- Burning Sensation: A burning sensation, particularly in the hands and feet, is another common symptom. This can be accompanied by redness and swelling in the affected areas.
- Digestive Issues: Autonomics can lead to digestive problems such as bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and nausea. These symptoms occur because the nerves that control the digestive system are not functioning properly.
- Bladder and Bowel Problems: Damage to the autonomic nerves can also affect bladder and bowel control, leading to incontinence or difficulty urinating.
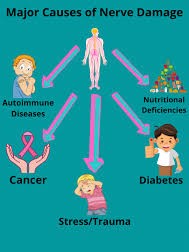
Causes of Nerve Damage
Nerve damage can result from a wide range of causes, including:
- Diabetes: Diabetes is one of the most common causes of nerve damage. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves over time, leading to diabetic neuropathy.
- Injuries: Physical injuries, such as those from car accidents, falls, or sports, can damage nerves directly or through compression.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as shingles, Lyme disease, and HIV, can cause nerve damage.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can lead to as the immune system attacks the nerves.
- Toxins: Exposure to toxins, such as heavy metals, chemicals, and certain medications, can damage nerves.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients, particularly B vitamins, can lead to nerve damage.
- Alcoholism: Chronic alcohol abuse can cause, known as alcoholic neuropathy.
- Cancer: Tumors can compress nerves, and certain cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, can also cause nerve damage.
- Genetic Disorders: Some genetic disorders, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, can lead to nerve damage.
Diagnosing Nerve Damage
If you suspect you have, it is essential to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will likely perform a series of tests to determine These tests may include:
- Physical Examination: Your doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination, checking for signs of muscle weakness, and loss of sensation.
- Neurological Examination: A neurological exam will assess your reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, and ability to feel sensations.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify underlying conditions that may be causing, such as diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, or infections.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of your muscles and can help determine if is affecting muscle function.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests measure how quickly electrical signals travel through your nerves, helping to identify.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, can help identify physical such as tumors or herniated discs.
Treatment Options for Nerve Damage
The treatment for nerve damage depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Some common treatment options include:
- Medications: Various medications can help manage. These may include pain relievers, anti-seizure medications, and antidepressants. In some cases, topical treatments such as lidocaine patches or capsaicin cream may be used to relieve localized pain.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength, coordination, and mobility. A physical therapist can design a customized exercise program to address your specific needs and help you regain function.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): TENS therapy involves the use of a small device that sends electrical impulses to the nerves through electrodes placed on the skin. This can help reduce pain and improve nerve function.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making healthy lifestyle changes can help manage and prevent further damage. This may include maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: If an underlying condition, such as diabetes or an autoimmune disease, is causing, it is essential to manage that condition effectively.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure or to remove a tumor that is causing nerve damage.
- Alternative Therapies: Some people find relief from symptoms through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or chiropractic care.
- Pain Management Techniques: Chronic pain can be challenging to manage. Pain management techniques such as mindfulness meditation, biofeedback, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can help you cope with pain and improve your overall well-being.
- Support Groups: Living with can be emotionally challenging. Joining a support group can provide you with a sense of community and help you connect with others who are facing similar challenges.
Preventing Nerve Damage
While not all cases of nerve damage can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Manage Chronic Conditions: If you have a chronic condition such as diabetes, it is essential to manage it effectively to prevent complications.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help protect your nerves.
- Protect Yourself from Injuries: Take precautions to avoid injuries that could damage your nerves, such as wearing protective gear during sports or using proper lifting techniques.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit your exposure to toxins that can damage nerves, such as heavy metals and certain chemicals.
- Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups can help detect and address potential issues before they lead to nerve damage.
Conclusion
Nerve damage can have a significant impact on your quality of life, but with the right knowledge and treatment, you can manage the symptoms and prevent them further. Recognizing the signs o early and seeking appropriate medical care is crucial for effective treatment. By making healthy lifestyle choices and managing underlying conditions, you can protect your nerves and maintain your overall health.