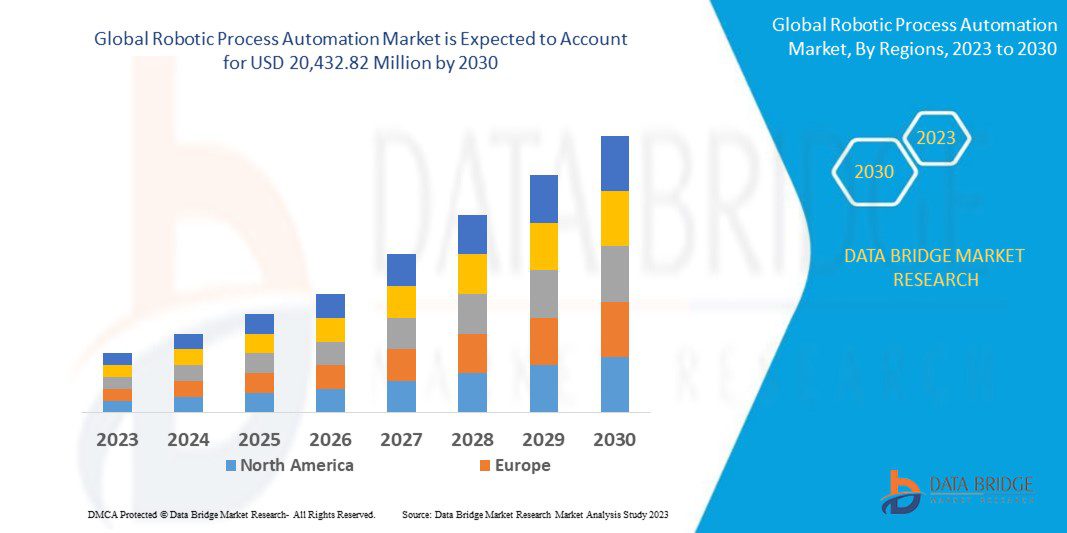
Introduction
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a transformative technology that automates repetitive tasks by leveraging software bots or “robots.” By mimicking human actions to perform rule-based tasks, RPA enables organizations to streamline operations, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency. Its applications span various industries, from banking and healthcare to manufacturing and customer service, revolutionizing workflows and allowing employees to focus on more strategic work.
This blog explores the essentials of RPA, its benefits and limitations, implementation strategies, and the future trends that are shaping the field.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
RPA is a technology that uses software robots to execute high-volume, repeatable tasks traditionally done by humans. Unlike physical robots, RPA bots work on digital platforms, interacting with applications, capturing and interpreting data, triggering responses, and communicating with other systems.
RPA technology is commonly applied in areas like:
- Data entry and validation
- Invoice processing
- Report generation
- Customer service support
- Inventory management
RPA functions within existing software systems without altering the core infrastructure, making it a cost-effective and non-intrusive solution for businesses aiming to enhance productivity and operational efficiency.
Acquire More Details: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-robotic-process-automation-market
Key Benefits of RPA
1. Increased Productivity
By automating repetitive tasks, RPA allows employees to concentrate on higher-value activities. This leads to greater productivity across departments, as bots can work continuously without downtime.
2. Improved Accuracy
RPA bots follow programmed instructions with precision, eliminating human errors that often occur in tasks like data entry and document processing. Enhanced accuracy improves the quality of work and reduces the need for rework.
3. Cost Savings
Automating tasks reduces the number of hours required to complete them, translating into substantial cost savings. Many companies report a rapid ROI on RPA projects as they are often less expensive to implement than larger automation initiatives.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
RPA is scalable; businesses can increase the number of bots to match workload demands without incurring significant costs. Additionally, RPA bots can be quickly reprogrammed to adapt to changing business needs, making it a flexible solution.
5. Enhanced Compliance
RPA bots follow regulatory protocols exactly as programmed, which is crucial in industries like finance and healthcare where compliance is critical. By maintaining thorough records of all activities, RPA helps companies adhere to regulatory requirements more easily.
6. Better Customer Experience
By freeing employees from repetitive tasks, RPA enables them to spend more time addressing customer needs, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
How Does RPA Work?
RPA bots operate by observing human actions on the computer interface, such as clicking buttons, entering data, and copying information. This process can be broken down into several steps:
- Process Mapping: A business process is analyzed to identify repetitive tasks suitable for automation.
- Bot Programming: Bots are programmed to mimic the actions performed by human users, using rules-based algorithms to complete each task.
- Execution and Monitoring: Bots are deployed to execute the tasks. Their performance is monitored to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
- Continuous Improvement: RPA processes can be optimized over time by refining the rules or updating the software to adapt to changing business needs.
RPA software can integrate with various applications such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) without the need for new infrastructure.
Applications of RPA Across Industries
1. Banking and Finance
- KYC (Know Your Customer) Processing: RPA bots automate customer verification by extracting and validating data, reducing onboarding time and ensuring compliance.
- Fraud Detection: Bots analyze transactions in real time, flagging suspicious activity based on programmed rules.
- Loan Processing: Automates the steps in loan applications, from document verification to credit score assessment.
2. Healthcare
- Patient Registration and Billing: RPA automates patient data entry, billing, and insurance claims, reducing errors and improving the patient experience.
- Appointment Scheduling: Bots streamline the appointment booking process, minimizing human error and reducing administrative time.
- Inventory Management: RPA ensures that hospitals and clinics maintain adequate inventory levels by tracking stock and generating orders as needed.
3. Retail and E-Commerce
- Order Processing: RPA speeds up order fulfillment by managing order entry, payment processing, and order tracking.
- Customer Support: Bots assist in handling customer inquiries, providing quick and consistent responses across multiple channels.
- Inventory Management: RPA helps manage stock levels, update inventory records, and communicate with suppliers.
4. Manufacturing
- Inventory and Supply Chain Management: RPA assists in monitoring inventory levels, processing orders, and maintaining supplier communication.
- Compliance Reporting: Automates the generation of compliance reports, ensuring regulatory requirements are consistently met.
- Quality Control: Bots analyze production data and identify defects, ensuring consistent product quality.
5. Human Resources
- Onboarding and Offboarding: RPA streamlines the onboarding process by automating document verification, data entry, and training schedules.
- Payroll Processing: Bots calculate salaries, manage tax withholdings, and process reimbursements, reducing errors and saving time.
- Employee Data Management: RPA updates employee records, monitors performance data, and generates reports as needed.
Challenges in Implementing RPA
1. Process Complexity
While RPA is ideal for repetitive, rule-based tasks, it struggles with more complex processes that require judgment or nuanced decision-making. Organizations may need to simplify or re-engineer processes before implementing RPA.
2. Initial Costs and ROI Concerns
The initial costs of RPA implementation can be high, especially for companies requiring custom solutions or large-scale deployment. Achieving a substantial ROI may take time, particularly if processes are not streamlined before automation.
3. Employee Resistance
Introducing RPA can cause apprehension among employees, who may fear job loss. Clear communication and training are essential to help employees understand RPA as a tool that complements their roles.
4. Maintenance and Scalability
As businesses grow, maintaining RPA systems and scaling them to match new workflows can be challenging. Bots may need regular updates to function correctly with software upgrades or changes in processes.
5. Security Risks
RPA bots often have access to sensitive data, posing a security risk if not properly managed. Ensuring data encryption, secure access protocols, and regular monitoring is critical for preventing unauthorized access.
Implementing RPA: Key Considerations
1. Identify Suitable Processes
Not all tasks are suitable for RPA. Target processes that are repetitive, rules-based, and involve structured data. Complex decision-making tasks may require additional support from AI or other technologies.
2. Choose the Right RPA Tools
Evaluate different RPA tools based on scalability, ease of integration, and compatibility with your organization’s existing systems. Popular RPA tools include UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism.
3. Pilot Program
Starting with a pilot program allows organizations to test RPA on a small scale, gather insights, and address challenges before a full-scale rollout. This approach helps refine processes and build employee confidence in the technology.
4. Engage Stakeholders
Involving stakeholders from the beginning ensures alignment across the organization. Include IT, operations, and end-users to build a comprehensive RPA strategy that considers all perspectives.
5. Monitor and Optimize
Once implemented, RPA bots should be monitored to ensure they perform as expected. Regular reviews and updates improve bot efficiency and allow for modifications to adapt to changing business needs.
Future Trends in Robotic Process Automation
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Combining RPA with AI enables bots to handle more complex tasks. AI-powered RPA can analyze unstructured data, make predictions, and enhance decision-making, extending automation to processes that were previously off-limits.
2. Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation refers to the application of multiple automation technologies, including RPA, AI, and machine learning, to achieve end-to-end automation of business processes. This approach helps companies automate even complex, multi-step processes.
3. Cloud-Based RPA
Cloud-based RPA solutions are gaining traction as they allow for greater scalability, remote access, and simplified maintenance. Cloud RPA also provides enhanced security and integrates seamlessly with cloud-native applications.
4. Low-Code/No-Code RPA Development
Low-code and no-code RPA platforms make it easier for non-technical users to develop and deploy bots, democratizing automation and accelerating RPA adoption across business units.
5. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Intelligent Document Processing combines RPA with natural language processing (NLP) to extract data from unstructured documents, such as invoices and contracts. This technology broadens the scope of automation, making it possible to handle a wider range of tasks.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation has become a cornerstone technology for modern enterprises, enabling them to streamline processes, reduce errors, and improve productivity. By automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, RPA allows businesses to shift focus toward strategic initiatives that drive growth. As advancements in AI, cloud computing, and low-code platforms continue to evolve, the potential applications of RPA will expand, offering new opportunities for businesses to innovate and enhance operational efficiency.